How Google and Bing Process Local Search DifferentlyMar192018

Local Search has definitely evolved, and now plays a key role in mobile searches in relation to sales. Statistics shows that 72% of consumers that performed a Local search, ultimately visited a place of business with five miles of their location. (Wordstream)
78% of people who performed Local searches on mobile resulted in making an offline purchase. (Search Engine Land)
Local search indexing and first page results vary between Google and Bing, but each is important to pay attention to for SEO long-term plans. Google holds the larger market share, but Bing has a lasting foothold.
In a Nutshell - Local Search Differences Between Google and Bing
Google Local search results serve up larger, established businesses/companies and appears to give preference to what they consider to be ‘credible’ results.
Bing Local search results produce smaller businesses and independent companies, when the search term includes a zip code or the searcher is seeking results closest to their location.
Instances Google Differs from Bing for SEO
301 & 302 Redirects
Google wants to see a 301 redirect, however, a 302 won’t cause a major indexing issue.
Bing wants to see a normal 301 direct. If a 302 Canonical redirect is used instead, Bing won’t follow the redirect, and most often doesn’t index the website.
Backlinks
Google likes clean, high authority backlinks and counts each one as a favorable vote.
Bing doesn’t focus on the number of backlinks but rather the quality of the backlink site.
Bing wants the inbound anchor text to be an exact match of the keywords, not so for Google.
Canonical Requirements
Google supports the use of the Canonical tag, used by site owners to avoid duplicate content issues.
Bing does not support the Canonical tag and doesn’t offer Canonical URL management in their Webmaster Center.
Indexing
Google crawls and indexes web pages deeper and faster compared to Bing.
Sub Domain Keywords
Google pays attention, while Bing doesn’t.
Meta Refresh (instant redirect)
Google follows a zero-second Meta refresh, and processes as a 301 redirect.
Bing sees a Meta Refresh and terminates their crawler from further indexing of the website. For Bing, best to use a normal 301 redirect.
On Page SEO
Google is intuitive about the context of each page.
Bing relies on specific keywords in page titles, page content and meta tags.
Page Size
Google requirements for page size is not set in stone.
Bing currently caches the first 100k of most web pages, with an average range of 95k-105k.
Social Media
Google doesn’t integrate social media well into their search results.
Bing fully integrates social media into their results. Example: If a friend in Facebook rates or recommends that page, it appears in search results quickly.
Bing vs Google
BrightLocal published an interesting analysis report about Bing vs Google, and some of the ‘Local’ highlights are listed below:
Which search engine gives more Page-One space to local businesses?
Generic Search Terms: (plumber, electrician, accountant, etc)
- With generic keywords, Google is more generous to local businesses.
- Google gives greater percentage of space to both Local Results (40%) & Local Business Sites (19%).
- Bing gives more space to larger websites (65% & 58% respectively).
Service Search Terms: (radiator repair, divorce attorney, etc)
- Fewer local results are displayed for Service Terms vs Generic Terms – larger websites benefit
- Google displays highest percentage of Local Results (32%)
- Bing displays highest percentage of Local Business Sites (32%)
- For ‘Service’ terms, Bing is the only search engine to give greater percentage of Page-One space to local businesses vs larger sites.
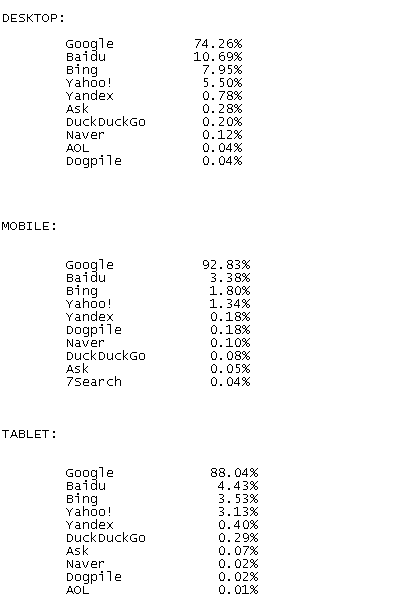
It's interesting to note the Search Engine Market Share various search engines held from 1/2017 through 1/2018. (data extracted via netmarket.com)