Tips for Using Google Search OperatorsSep172018

Definition : Search Operator
A Search Operator (or search parameter) is a character or string of commands and characters used in a search engine query to narrow the focus of the search.
Using Search Operators help you search quickly for information plus can find information to assist with SEO, identify errors that may exist on your site, and may also reveal information about competitor websites and activity.
Find Social Media Profiles of People You Want to Reach Out to:
Enter into Google search field:
paula pierce hosting (site:twitter.com | site:facebook.com | site:linkedin.com)
Here are the results:
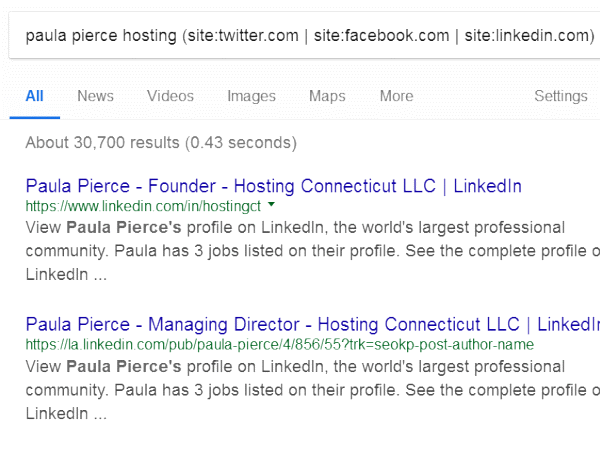
Let’s do one more. Just enter a name and occupation/field to see if you can locate the social media information for that person or company you want to connect with.
brad pitt actor (site:twitter.com | site:facebook.com | site:linkedin.com)
Here are the results:
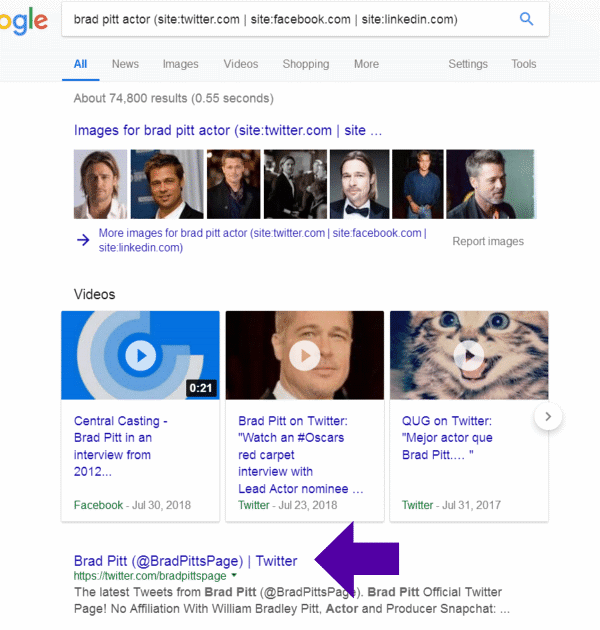
One more example:
dennis muilenburg boeing (site:twitter.com | site:facebook.com | site:linkedin.com)
Here are the results for Dennis Muilenburg, CEO Boeing:
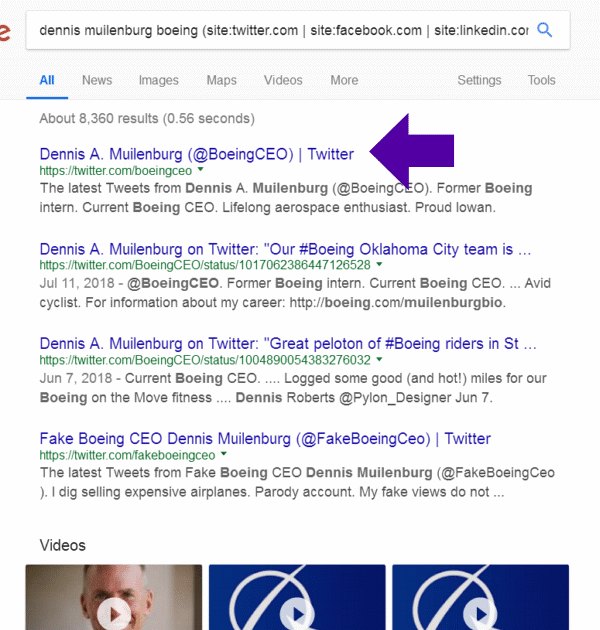
Find How Often Competitors are Publishing New Content
Blog files are usually stored in a subfolder or under a subdomain.
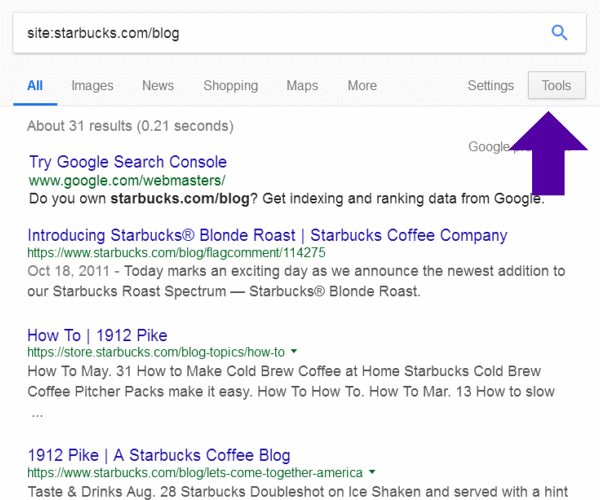
search: site:starbucks.com/blog
Placing “blog” after the domain brought results:
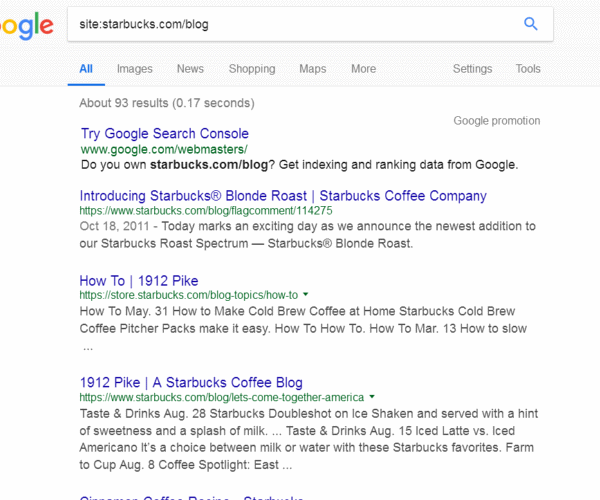
And another search:
site:blog.starbucks.com
Placing “blog.” in front of the domain yielded no results:
Use Google Tools tab to see how often content has been published.
Click on the Tools tab, upper Right:
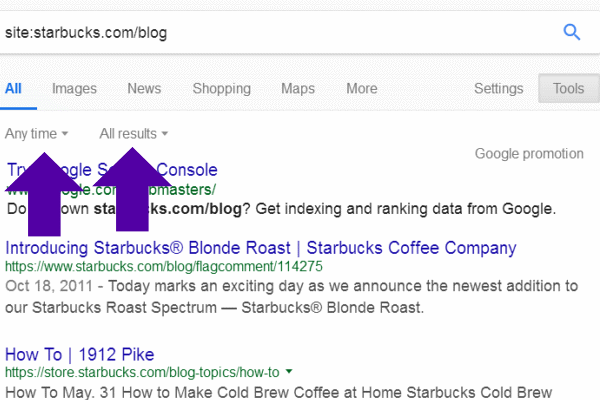
Any Time and All Results become visible:
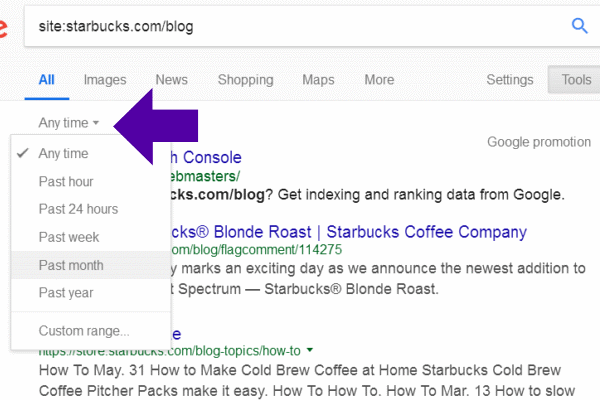
Click on “Any Time” and select the time frame for articles/content published, i.e. 24 hours, one month, one year, etc, or assign a Custom Range:
Find Specific Search Terms in Blog Titles
Use the variable inposttitle:
inposttitle:white kitchen makeover
Find Text in Blog Content
Use the variable allintitle:
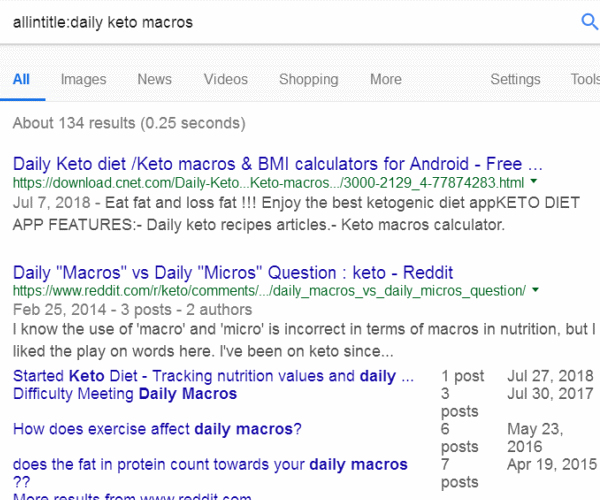
allintitle:daily keto macros
Results:
Find Target Results for Specific Search Phrases
Use the variable intitle:
intitle:plaid shoes for women
Find Phrases With Exact Match Results
Use the Quote variable “ ”
“womens blue plaid shoes”
Find Duplicate Content On a Site
Use the variable site:
site:hostingct.com “website hosting”
Find if Your Brand is Associated with Other TLD’s
It’s optimal to register all TLD’s for your Brand. If you only have the .com registered for your Brand, you may want to know if any other people or businesses are infringing on your Brand. The -site is excluding search for your .com domain.
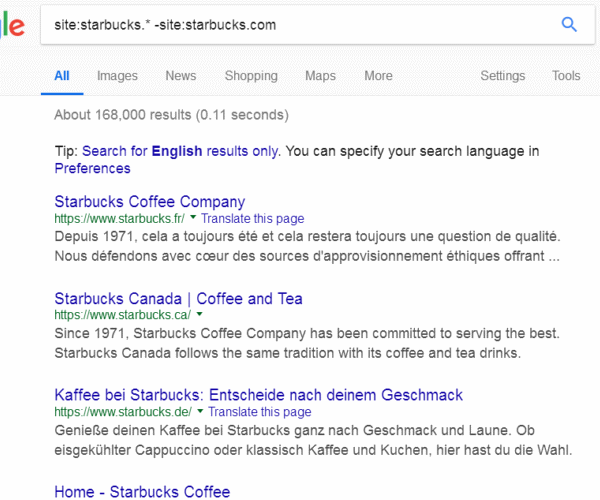
site:starbucks.* -site:starbucks.com
Results:
Common Search Operator Commands
Most people enter a search term as:
Variations on this simple search:
the variable OR
howard OR shultz
Can also use the | symbol instead of the text OR
howard | Schultz
Returns results related to howard or schultz, or both.
the variable AND
howard AND schultz
Returns results related to both howard and shultz
the variable -
howard –starbucks
Returns exclude a phrase or term, results will relate to howard, but not to Starbucks (the business).
the variable *
howard * starbucks
The * symbol as a wildcard and will match any word or phrase.
the variable ( )
(frappuccino OR latte) starbucks
Use to group multiple terms to control how the search is executed.
AROUND ( )
womens plaid AROUND(2) shoes
Narrow results where two or more terms appear on the page and display close to each other.
the variable $
starbucks $5
Returns results for prices.
Preface a search with allintext:
allintext:starbucks howard Schultz
Returns only those results containing all of the specified words in the page content.
Preface a search with allintitle:
allintitle: starbucks frappe
Returns only those results that contain all of the specified words in the title tag.
Preface a search with allinurl:
allinurl:starbucks latte
Returns those results only containing all of the specified words in the URL.
Preface a search with cache:
cache:starbucks.com
Returns the most recent cached version of an indexed webpage.
Preface a search with define:
define:starbucks
Returns the meaning of a word drawing on the Google built-in dictionary.
Search with filetype: or ext:
starbucks filetype:pdf starbucks ext:pdf
Returns results limited to certain filetypes of pdf, txt, ppt, docx.
Both filetype: and ext: returns the same results.
Search with in
tbs in ounce
Results will be the conversion to currencies, weights, temperatures, etc.
Preface a search with intext:
intext:starbucks howard Schultz
Returns page results containing any of the specified words in the content.
Preface a search with intitle:
intitle:starbucks frappe
Returns results with either, or any of the specified words in the title.
Preface a search with inurl:
inurl:starbucks frappe
Returns pages with either or any of the specified words in the URL.
Preface a search with map:
map:98118
Results returned showing map of the area searched. Enter a zip code, city, town, state, landmark, etc.
Preface a search with related:
related:starbucks.com
Returns results related to a domain name.
Preface a search with site:
site:starbucks.com
Returns results only to those of the searched website.
Preface a search with stocks:
stocks:SBUX
Returns stock information for the specified stock symbol.
Preface a search with weather:
weather:phoenix
Returns results for a specified location. You can also enter a zip code: weather:98118
note:
Over the years Google has deprecated the functionality of many of the traditional operators. The deprecated operators will return results, but at best they are hit and miss results. The Search Operator list above (as of 2018) are functional.
Additional resources:
Bing Official Search Operators:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff795620.aspx
Google Official Search Operators:
https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/2466433?hl=en




